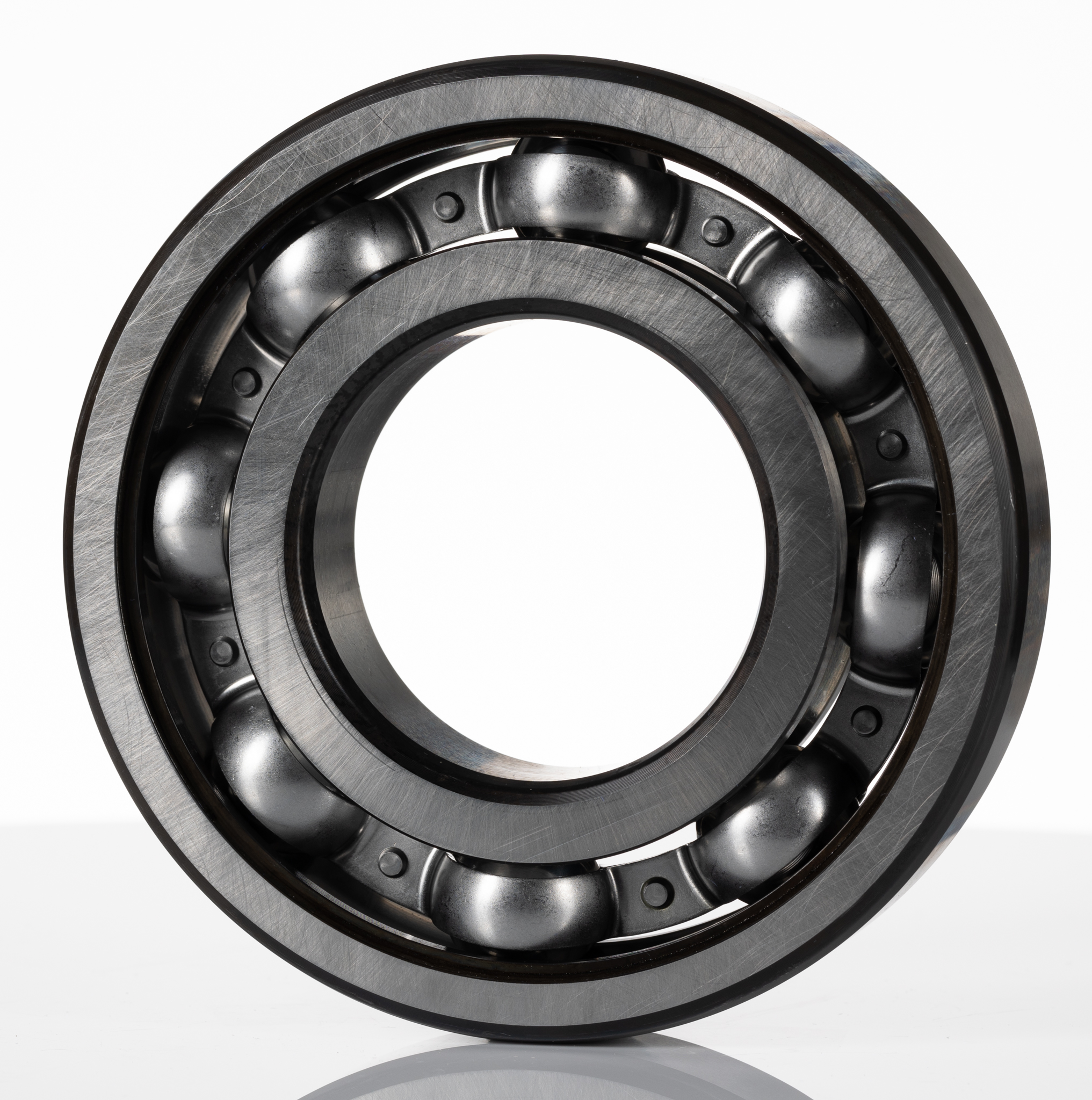
Are you tired of friction holding your machines back? Unwanted friction wastes energy and causes wear. Ball bearings are the solution to this pervasive problem.
Ball bearings reduce friction and allow smooth rotational movement in machinery. They support radial and axial loads, making parts move freely and efficiently.
I recall visiting an old factory once. The machinery groaned and vibrated. It was clear they needed better friction management. This is where quality bearings make a huge difference.
How Do Ball Bearings Work to Reduce Friction?
Understanding their design helps explain their efficiency. Bearings are simple yet brilliant.
Ball bearings reduce friction by allowing rolling elements (balls) to carry the load, converting sliding friction into rolling friction, which generates less heat and wear.

The Ingenious Mechanism of Ball Bearings
It is fascinating to see how these small components achieve such a big impact. As a bearing manufacturer, I’ve seen countless designs.
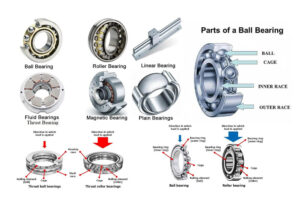
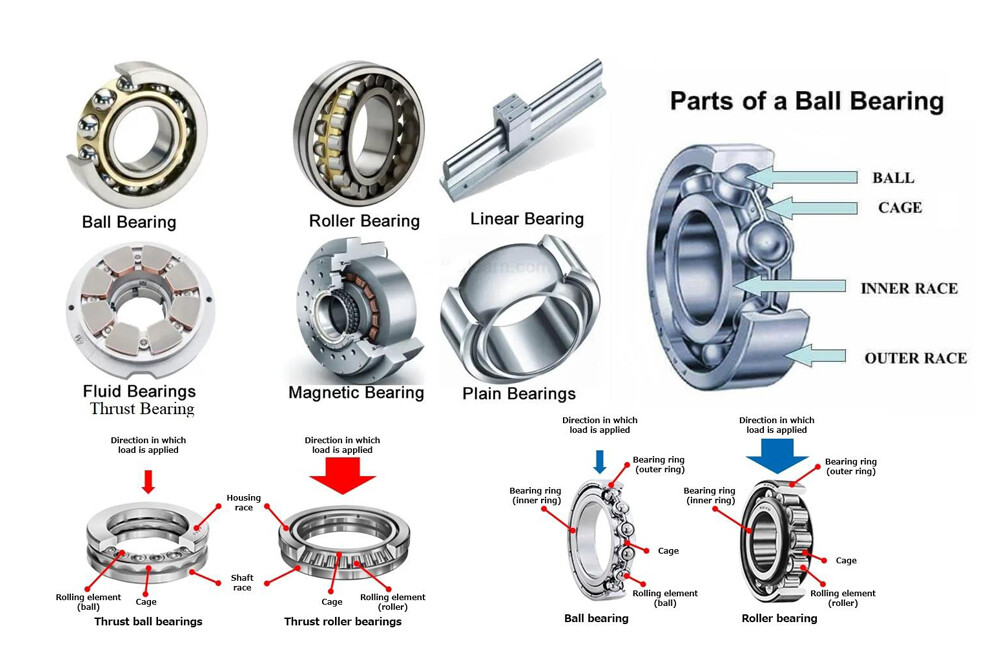
- Components: A ball bearing consists of several key parts.
- Outer Ring: This is the stationary part. It is typically fixed to a housing.
- Inner Ring: This is the rotating part. It is usually attached to a shaft.
- Balls (Rolling Elements): These are precision-ground spheres. They run between the inner and outer rings.
- Retainer (Cage): This separates the balls. It maintains even spacing between them.
- Rolling vs. Sliding Friction: This is the core principle.
- Sliding Friction: When two surfaces rub against each other. This creates a lot of heat and resistance. Imagine pushing a heavy box across the floor.
- Rolling Friction: When one object rolls over another. This produces much less resistance. Imagine rolling that same box on wheels.
- Load Distribution: How forces are shared.
- The balls distribute the load evenly. Each ball takes a share of the weight.
- This prevents excessive pressure points. It protects the surfaces of the rings.
- Lubrication: Essential for smooth operation.
- Grease or oil is used to reduce friction further. It also dissipates heat.
- Proper lubrication extends bearing life. It prevents corrosion.
What Types of Loads Do Ball Bearings Handle Best?
Bearings are designed for specific force types. Knowing these helps you pick the right one.
Ball bearings are primarily designed to handle radial loads (perpendicular to the shaft) and moderate axial loads (parallel to the shaft), making them versatile for many applications.
Understanding Load Types and Bearing Capabilities
Choosing the right bearing means matching it to the forces it will encounter. I always guide customers through this.
- Radial Loads: Forces pushing directly downwards or upwards on the bearing.
- Think of a car wheel. The weight of the car creates a radial load on the wheel bearings.
- Ball bearings excel at supporting radial loads. Their design allows for efficient transfer of vertical force.
- Axial Loads (Thrust Loads): Forces pushing along the axis of rotation.
- Imagine a spinning top. The force pushing down on its point is an axial load.
- Standard ball bearings can handle some axial loads. Deep-groove ball bearings offer good axial capacity in both directions.
- Combined Loads: A mix of radial and axial forces.
- Many applications involve both. For instance, a drill press experiences both.
- Specialized ball bearings, like angular contact ball bearings, are designed for high combined loads.
- Impact Loads: Sudden, sharp forces.
- Ball bearings generally do not handle high impact loads well. The balls can deform.
- For impact loads, roller bearings are often a better choice.
- Bearing Selection Table:
| Load Type | Best Bearing Type | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Radial | Deep-Groove Ball Bearing | Electric Motor Shaft |
| Pure Axial | Thrust Ball Bearing | Turntable |
| Combined | Angular Contact Ball Bearing | Car Wheel Hub |
| High Impact | Cylindrical Roller Bearing | Gearbox |
Where Are Ball Bearings Commonly Used Today?
Ball bearings are everywhere. From small gadgets to large machinery, they make our world go round.
Ball bearings are widely used in diverse applications, including automotive parts, electric motors, household appliances, industrial machinery, and even consumer electronics, due to their efficiency in reducing friction and enabling smooth motion.
A World Powered by Smooth Rotation
It’s amazing how a small component can have such a broad impact. My products go into many different industries.
- Automotive Industry: A car uses many bearings.
- Wheel Bearings: These allow wheels to spin freely. They handle tough radial and axial loads.
- Engine Bearings: Inside the engine, they support crankshafts and camshafts. This ensures smooth power delivery.
- Transmission Bearings: These enable gears to shift smoothly. They manage rotational forces.
- Electric Motors: Bearings are fundamental to motor operation.
- Rotor Support: They support the motor’s rotating part. This reduces friction and vibration.
- Efficiency: Good bearings mean less energy loss. This makes motors more efficient.
- Household Appliances: Look around your home; bearings are hidden everywhere.
- Washing Machines: They support the drum. Without them, the drum would clang.
- Vacuum Cleaners: Bearings are used in the brush rolls. They ensure smooth rotation and effective cleaning.
- Blenders: They allow the blades to spin at high speeds.
- Industrial Machinery: Factories rely heavily on bearings.
- Conveyor Belts: Bearings keep them moving. They handle constant loads.
- Pumps and Fans: They ensure smooth, continuous operation. This prevents breakdowns.
- Machine Tools: Precision grinders and lathes depend on accurate bearings. This ensures precise cuts.
- Consumer Electronics: Even tiny devices use bearings.
- Computer Hard Drives: Once common, tiny bearings were crucial for spinning platters.
- Drones: Bearings in the motors help propellers spin fast. They reduce vibration.
What Factors Influence Ball Bearing Performance and Lifespan?
Even the best bearings can fail if not properly used. Many factors affect how long a bearing lasts.
Ball bearing performance and lifespan are significantly influenced by factors such as proper lubrication, correct installation, managing operating temperature, controlling load conditions, and protecting them from contamination.
Maximizing Bearing Life and Efficiency
I always tell my customers that a good bearing is only as good as its environment.
- Lubrication Quality and Quantity: This is perhaps the most important factor.
- Right Lubricant: Using the correct type of grease or oil for the application. Different speeds and temperatures need different lubricants.
- Enough Lubricant: Too little lubrication causes wear. Too much can cause overheating.
- Clean Lubricant: Contaminated lubricant harms the bearing.
- Installation Accuracy: How the bearing is put into place.
- Proper Fit: Bearings must fit snugly. Too loose, they slip. Too tight, they pre-load incorrectly.
- Alignment: Misalignment causes uneven loading. This reduces life.
- Proper Tools: Using presses instead of hammers to install. This prevents damage.
- Operating Temperature: Heat is the enemy of bearings.
- Optimal Range: Bearings perform best within a specific temperature range.
- Overheating: High temperatures degrade lubricant quickly. They can also permanently damage the steel.
- Cooling: Adequate cooling is essential in high-speed or high-load applications.
- Load Conditions: The forces the bearing experiences.
- Overloading: Applying too much weight or force. This causes premature fatigue.
- Impact Loads: Sudden, sharp forces. These are very damaging.
- Vibration: Excessive vibration leads to wear and fatigue.
- Contamination Control: Keeping dirt and moisture out.
- Dust and Dirt: Abrasive particles get between rolling elements. They cause wear.
- Moisture: Water causes rust. It breaks down lubricants.
- Sealing: Effective seals protect the bearing interior.
Conclusion
Ball bearings are crucial for smooth rotation. They efficiently manage friction in many machines. Proper selection and maintenance ensure their long and effective use.